Element no 22 crossword clue – Prepare to unravel the captivating enigma of element no. 22, titanium, as we delve into its remarkable properties, applications, and biological significance. This multifaceted element promises an enthralling journey, revealing its secrets through the lens of a crossword clue.
Titanium’s position in the periodic table, its unique characteristics, and its diverse roles in industries and biological systems await our exploration. Join us as we unravel the intriguing world of element no. 22.
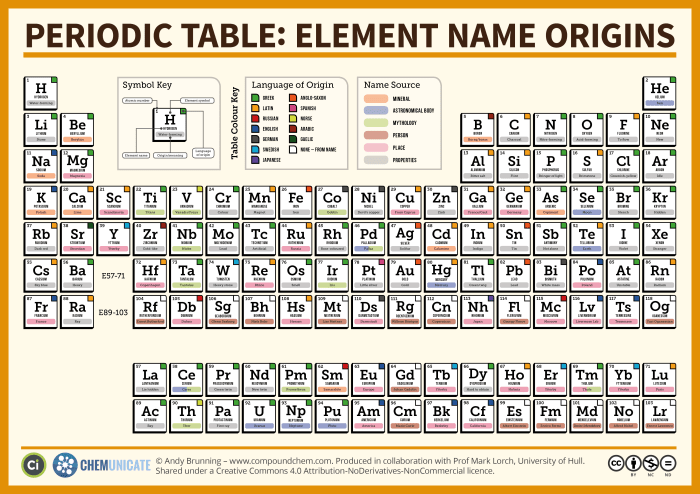
Element No. 22: Titanium

Titanium, an extraordinary metal, holds the atomic number 22, symbolized by ‘Ti’ on the periodic table. With an atomic weight of 47.867, titanium stands out for its exceptional properties and wide-ranging applications.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
Titanium possesses a unique combination of physical and chemical attributes. It is incredibly strong, exhibiting a high strength-to-weight ratio comparable to steel. Its exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion make it a valuable material in demanding environments. Additionally, titanium is non-magnetic and has a low thermal conductivity, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Titanium in the Periodic Table

Titanium is an element with the atomic number 22. It is located in Group 4 (previously known as Group IVB) and Period 4 of the periodic table. This placement signifies its unique chemical properties and characteristics.
Elements within the same group (vertical column) share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons. As we move down a group, the atomic radius generally increases because of the addition of new energy levels. Titanium is no exception, with a relatively large atomic radius compared to other elements in its group.
Electronegativity, a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons, generally decreases down a group. This is because the valence electrons are farther away from the nucleus as we move down the group. Titanium has a relatively low electronegativity compared to other elements in its group.
Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, generally increases across a period (horizontal row). This is because the effective nuclear charge increases as we move from left to right across a period. Titanium has a relatively high ionization energy compared to other elements in its period.
Similarities and Differences with Neighboring Elements
Titanium shares some similarities with its neighboring elements in the periodic table. For example, it is a transition metal, meaning it has partially filled d orbitals. Like other transition metals, titanium can exhibit variable oxidation states and form complex ions.
Element no 22 crossword clue can be solved by thinking about a cap hold. This legal term, explained in detail on the cap hold and renounce rights page, refers to a situation where a team can retain a player’s rights even after their contract expires.
So, for element no 22 crossword clue, think about the element that can hold and renounce rights.
However, titanium also has some unique properties that distinguish it from its neighbors. For instance, it is highly resistant to corrosion, making it a valuable material for various industrial applications. Additionally, titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it useful in aerospace and medical applications.
Titanium’s Role in Biological Systems
Titanium plays a crucial role in biological systems, particularly in the human body. Its unique properties make it an ideal material for various medical applications, but it also has potential biological effects that warrant consideration.
Titanium in the Human Body
Titanium is not naturally found in the human body, but it can be introduced through various sources, such as medical implants, dental materials, and occupational exposure. Once in the body, titanium tends to accumulate in tissues like bone, liver, and spleen.
Medical Applications of Titanium Implants
Titanium is widely used in medical implants due to its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. These implants include:
- Joint replacements (e.g., hip, knee)
- Dental implants
- Trauma plates and screws
- Cardiovascular devices (e.g., heart valves)
Titanium implants offer several advantages, including:
- Excellent longevity and durability
- High resistance to infection
- Reduced risk of allergic reactions
Potential Biological Effects of Titanium Exposure
While titanium is generally considered biocompatible, long-term exposure can have both beneficial and adverse effects:
- Beneficial Effects:Titanium has been shown to stimulate bone growth and promote tissue regeneration, making it a valuable material for orthopedic applications.
- Adverse Effects:Prolonged exposure to titanium particles can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and potentially cancer in certain animal models. However, the clinical significance of these findings in humans is still being debated.
Titanium Extraction and Production
Titanium is primarily extracted from its principal ore, ilmenite, which contains titanium dioxide (TiO2). The extraction process involves several complex steps:
Kroll Process
The Kroll process is the most widely used method for producing titanium metal. It involves reducing titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) with magnesium in an inert atmosphere. The reaction produces titanium metal and magnesium chloride as a byproduct:
TiCl4 + 2Mg → Ti + 2MgCl2
Hunter Process
The Hunter process is an alternative method for producing titanium metal. It involves reducing titanium dioxide (TiO2) with carbon in an electric arc furnace. The reaction produces titanium metal and carbon monoxide as a byproduct:
TiO2 + 2C → Ti + 2CO
Challenges in Titanium Extraction and Production
Titanium extraction and production face several challenges:
- High Energy Requirements:Both the Kroll and Hunter processes require significant amounts of energy, making titanium production an energy-intensive process.
- Environmental Concerns:The production of titanium can release harmful pollutants, such as chlorine and carbon monoxide, into the environment.
- High Cost:The complexity of the extraction and production processes, combined with the high energy requirements, makes titanium a relatively expensive metal.
Global Distribution of Titanium Resources and Major Producers, Element no 22 crossword clue
Titanium resources are found in various parts of the world, with significant deposits in:
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- South Africa
- United States
The major producers of titanium include:
- China
- Russia
- Japan
- United States
- Kazakhstan
Helpful Answers: Element No 22 Crossword Clue
What is the atomic number of titanium?
22
What is titanium’s symbol?
Ti
What is titanium’s most common application?
Aerospace industry