Prepare to delve into the enigmatic world of double take dual court systems, a fascinating legal landscape where justice unfolds in two distinct arenas. As we embark on this journey, we’ll unravel the historical origins, structural organization, and intricate interplay of these systems.
From the hallowed halls of ancient Greece to the modern-day complexities of contemporary societies, dual court systems have played a pivotal role in shaping legal frameworks and ensuring access to justice. Brace yourself for a captivating exploration of their advantages, disadvantages, and the profound impact they have on the administration of justice.
Legal Framework
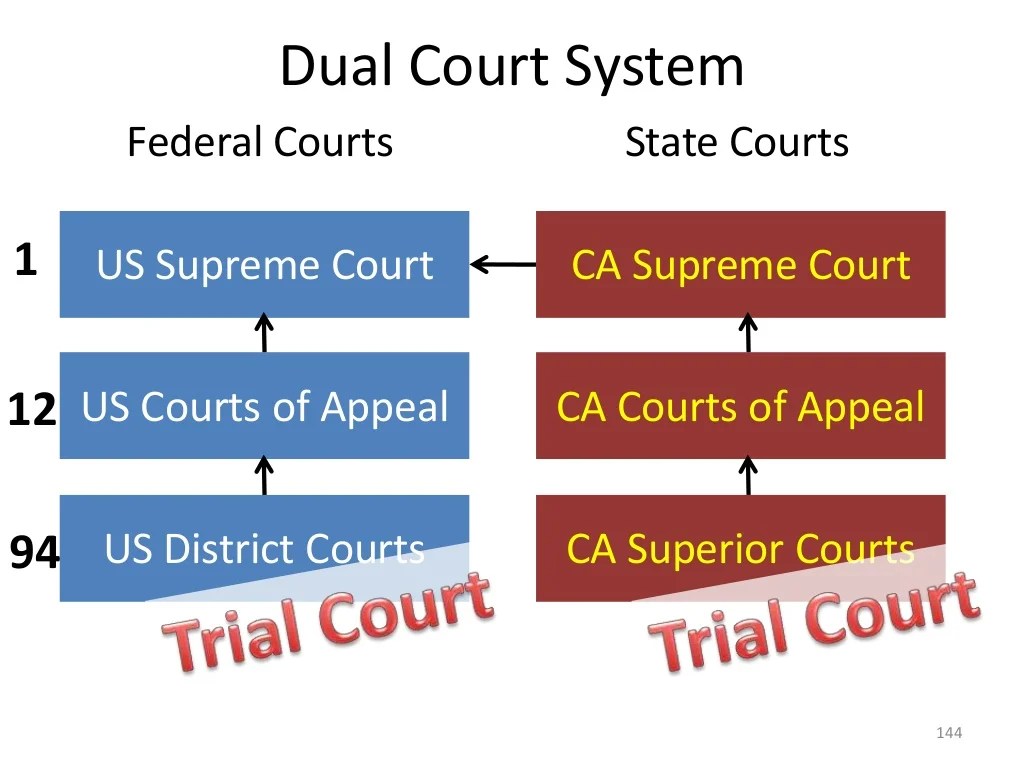
A dual court system refers to a legal system that operates with two distinct sets of courts: one for general civil and criminal cases and the other for specialized matters such as tax, labor, or administrative law.
The concept of dual court systems has been implemented in various countries worldwide, including France, Germany, Italy, and Japan. These systems typically have a lower court level that handles minor offenses and civil disputes, while a higher court level is responsible for more serious cases and appeals.
Historical Development, Double take dual court system
The historical development of dual court systems can be traced back to the Roman Empire, where separate courts existed for civil and criminal matters. During the Middle Ages, this concept was adopted by various European countries, with the emergence of specialized courts for ecclesiastical, commercial, and maritime law.
Structural Organization: Double Take Dual Court System
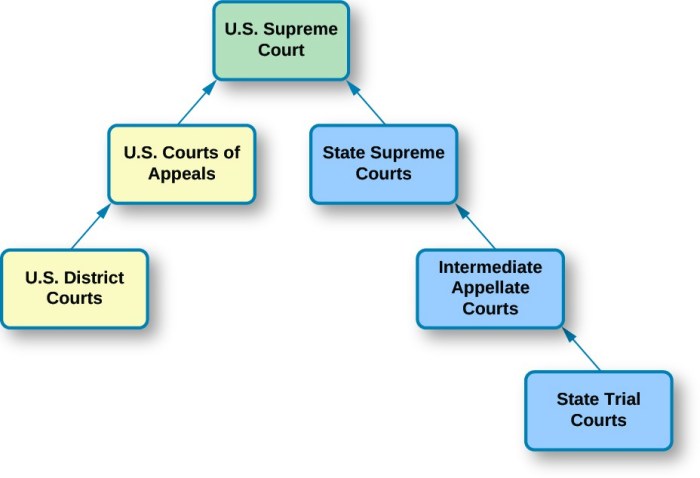
Double take dual court systems consist of two separate court systems: the trial court system and the appellate court system. Each system has its own distinct roles and responsibilities, and they work together to ensure that justice is served.
The trial court system is responsible for hearing cases and making decisions based on the evidence presented. The appellate court system is responsible for reviewing decisions made by the trial court system and ensuring that they were made in accordance with the law.
Relationship between the Two Court Systems
The trial court system and the appellate court system are closely related. Decisions made by the trial court system can be appealed to the appellate court system, which can then overturn or uphold the original decision. This system of checks and balances helps to ensure that justice is served and that the law is applied fairly.
Jurisdiction and Case Allocation

The double take dual court system allocates cases based on specific criteria to determine which court has jurisdiction. The type of case, the amount of damages claimed, and the location of the incident are key factors in determining jurisdiction.
Cases in Each Court System
Generally, minor offenses and civil disputes involving claims below a certain amount are handled in the lower court system. These may include traffic violations, misdemeanors, and small claims cases.
The higher court system handles more serious offenses, such as felonies, complex civil disputes involving substantial damages, and appeals from the lower courts.
Transfer of Cases
In certain circumstances, cases may be transferred between the two court systems. For instance, a case may be transferred from the lower court to the higher court if the charges are upgraded or the damages claimed exceed the lower court’s jurisdiction.
Similarly, a case may be transferred from the higher court to the lower court if the charges are reduced or the damages claimed fall below the higher court’s jurisdiction.
Judicial Independence
Judicial independence is a fundamental principle of double take dual court systems. It ensures that judges are free from external influences and can make impartial decisions based solely on the law and the facts of the case.There are several mechanisms in place to safeguard judicial independence in these systems.
First, judges are typically appointed by an independent body, such as a judicial council or commission. This process helps to ensure that judges are selected on the basis of their qualifications and experience, rather than their political affiliations or personal connections.Second,
judges have secure tenure. Once appointed, they can only be removed from office for cause, such as misconduct or incompetence. This protection helps to shield judges from political pressure and allows them to make decisions without fear of retaliation.Third, there are mechanisms in place for holding judges accountable for their conduct.
These mechanisms include judicial disciplinary boards and the power of judicial review. Judicial disciplinary boards can investigate complaints of misconduct against judges and recommend sanctions, including removal from office. Judicial review allows higher courts to review the decisions of lower courts and ensure that they are consistent with the law.These
mechanisms work together to ensure that judges are independent and impartial. They help to protect the integrity of the judicial process and ensure that all citizens have access to fair and impartial justice.
Judicial Appointments
The process for appointing judges varies from one double take dual court system to another. In some systems, judges are appointed by the executive branch of government, while in others they are appointed by the legislature. In some cases, judges are elected by the public.Regardless
of the method of appointment, it is important that the process is fair and transparent. This helps to ensure that judges are selected on the basis of their qualifications and experience, rather than their political affiliations or personal connections.
Judicial Tenure
Once appointed, judges typically have secure tenure. This means that they can only be removed from office for cause, such as misconduct or incompetence. This protection helps to shield judges from political pressure and allows them to make decisions without fear of retaliation.The
length of judicial tenure varies from one system to another. In some systems, judges serve for life, while in others they serve for a fixed term. The length of tenure should be long enough to provide judges with sufficient independence, but not so long that they become unresponsive to the needs of the public.
Mechanisms for Holding Judges Accountable
There are several mechanisms in place for holding judges accountable for their conduct. These mechanisms include judicial disciplinary boards and the power of judicial review.Judicial disciplinary boards are typically composed of judges and other legal professionals. They investigate complaints of misconduct against judges and recommend sanctions, including removal from office.Judicial
review allows higher courts to review the decisions of lower courts and ensure that they are consistent with the law. This power helps to ensure that judges are making fair and impartial decisions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Double take dual court systems offer both advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these factors is crucial when evaluating the system’s effectiveness.
One advantage of double take dual court systems is their potential to enhance access to justice. By providing two distinct courts, these systems can cater to a broader range of legal issues and cater to the needs of diverse populations.
The double take dual court system, where a case can be tried twice, has been a topic of debate for years. While the system has its supporters, there are also those who believe it can lead to inconsistencies in the legal process.
Just as an anti pawing device for horses can prevent a horse from engaging in a specific behavior, the double take dual court system aims to prevent inconsistent outcomes in legal cases.
Advantages
- Enhanced access to justice for marginalized communities
- Increased efficiency in resolving disputes
- Reduced costs for litigants
- Improved public confidence in the legal system
For instance, in Canada, the double take dual court system has been credited with improving access to justice for Indigenous communities by establishing specialized courts that consider cultural and traditional laws.
Disadvantages
- Potential for increased complexity and delays
- Challenges in coordinating between different courts
- Risk of inconsistent rulings and interpretations
- Additional costs associated with maintaining two separate court systems
On the other hand, double take dual court systems can also pose challenges. One potential disadvantage is the increased complexity and potential for delays in resolving disputes. With two separate courts, there is a risk of cases being transferred back and forth, leading to extended proceedings.
Comparative Analysis
Double take dual court systems stand out from other court systems in several ways. Let’s explore these differences and their implications for justice administration.
Structure
Double take dual court systems feature two distinct court structures: the “take one” court and the “take two” court. The “take one” court handles less complex cases, while the “take two” court addresses more intricate matters. This specialization allows for efficient case processing and targeted expertise in handling different case types.
Jurisdiction
Double take dual court systems divide jurisdiction based on case complexity and severity. The “take one” court typically has jurisdiction over less serious offenses and civil disputes, while the “take two” court handles major crimes, complex civil cases, and appeals from the “take one” court.
This division ensures that cases are assigned to courts with appropriate expertise and resources.
Operation
Double take dual court systems often employ different procedures and rules for the “take one” and “take two” courts. The “take one” court may have simplified procedures, expedited trials, and limited discovery options to facilitate quick resolution of less complex cases.
In contrast, the “take two” court may adopt more formal procedures, extensive discovery, and complex evidentiary rules to accommodate the intricate nature of the cases it handles.
Current Trends and Future Developments
Double take dual court systems are evolving to meet changing societal needs and technological advancements. Several trends are shaping their development, including:
- Increased use of technology: Courts are increasingly using technology to improve efficiency, access to justice, and transparency. This includes the use of electronic filing, video conferencing, and artificial intelligence.
- Growing focus on specialized courts: There is a trend towards creating specialized courts to handle specific types of cases, such as family law, business law, and environmental law. This allows for judges to develop expertise in particular areas and provide more tailored and efficient justice.
- Expansion of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) methods: ADR methods, such as mediation and arbitration, are becoming more popular as ways to resolve disputes outside of the traditional court system. This can help to reduce costs, delays, and stress for parties involved.
Emerging Issues and Challenges
While double take dual court systems offer potential benefits, they also face several challenges:
- Cost and complexity: Implementing and maintaining double take dual court systems can be expensive and complex. This includes the cost of training judges and staff, developing and implementing new technologies, and ensuring access to justice for all.
- Potential for bias: There is a risk that double take dual court systems could lead to bias, as judges in different courts may have different perspectives and experiences.
- Need for coordination and cooperation: Effective double take dual court systems require coordination and cooperation between different courts and levels of government. This can be challenging to achieve in practice.
Potential Future Directions
The future of double take dual court systems is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including:
- Continued technological advancements: Technology will continue to play a major role in the development of double take dual court systems. This could include the use of artificial intelligence to assist judges in making decisions, the development of virtual courtrooms, and the use of blockchain technology to improve transparency and security.
- Growing demand for specialized courts: The demand for specialized courts is likely to continue to grow as society becomes more complex and specialized. This could lead to the creation of new courts to handle specific types of cases, such as cybercrime, intellectual property, and environmental law.
- Increased focus on access to justice: There is a growing recognition of the need to improve access to justice for all. This could lead to the development of new programs and initiatives to help people navigate the court system and afford legal representation.
User Queries
What is the primary distinction between a double take dual court system and other court systems?
Double take dual court systems are unique in their dual structure, comprising two distinct court systems that handle different types of cases and jurisdictions.
How does a double take dual court system ensure judicial independence?
These systems often implement measures such as judicial appointments by independent bodies, fixed terms of office, and mechanisms for holding judges accountable, ensuring their impartiality and freedom from political influence.
What are the key advantages of double take dual court systems?
They offer potential advantages such as specialized expertise in different areas of law, increased efficiency in case handling, and enhanced access to justice for diverse populations.
What are the potential disadvantages associated with double take dual court systems?
These systems may face challenges such as increased complexity, potential for jurisdictional conflicts, and resource allocation issues.
How are cases allocated between the two court systems in a double take dual court system?
Criteria for case allocation vary depending on the specific system, but often involve factors such as the nature of the case, the severity of the offense, and the potential impact on society.